Contents:What is game design?
What is game design? Game design is a fascinating and rapidly evolving field that has seen explosive growth in recent years. From blockbuster video games like Fortnite and Minecraft to indie hits like Among Us and Stardew Valley, games have become an integral part of our culture and entertainment landscape. However, behind every successful game is a talented team of game designers, artists, and programmers who have spent countless hours designing, prototyping, and iterating on the game’s mechanics, aesthetics, and dynamics.
In this post, we’ll take a deep dive into the world of game design, exploring what it is, why it’s important, and how it’s done. We’ll cover the key elements of game design, the game design process, and the tools and skills needed to create successful games. Whether you’re a budding game designer, a curious gamer, or simply someone who wants to learn more about this exciting field, this post will provide a comprehensive and detailed overview of game design. So let’s jump in and explore the world of game design together!
What is Game Design Key takeaways
- What is game design?
- Game design is the process of creating rules, mechanics, objectives, and other elements that make up a game.
- It involves designing game mechanics, dynamics, and aesthetics to create an engaging interactive experience.
- Elements of Game Design:
- Mechanics: The rules and systems that govern gameplay.
- Dynamics: The emergent patterns of behavior from player interactions with the mechanics.
- Aesthetics: The visual, auditory, and storytelling elements that contribute to the player’s experience.
- Game Design Process:
- Idea Generation: Brainstorming, research on audience and trends.
- Prototyping: Paper prototypes and digital prototypes to test mechanics.
- Playtesting: Testing the game with real players to identify issues and gather feedback.
- Iteration: Making changes and improvements based on playtesting feedback.
- Game Design Tools:
- Game Engines: Unity, Unreal Engine, Godot.
- 2D/3D Art Tools: Photoshop, Blender, Maya.
- Sound Design Tools: Fmod, Wwise, Audacity.
- Game Design Careers:
- Game Designer: Creates game concepts, mechanics, and oversees development.
- Game Artist: Creates visual assets like characters, environments, animations.
- Game Programmer: Implements game mechanics and features through coding.
- Importance and Future of Game Design:
- Well-designed games are essential for engaging and retaining players.
- Future trends include VR/AR, mobile gaming, esports, and applications beyond entertainment.
I. Introduction
Game design is the process of creating rules, mechanics, objectives, and other elements that make up a game. It is the art and science of developing a game, from its initial concept to the final product. Game design is an interdisciplinary field that incorporates elements of psychology, storytelling, mathematics, computer science, and visual arts.
A. Definition of game design
Game design involves a wide range of activities, from ideation to prototyping to testing and iteration. It encompasses many different aspects of game creation, including:
- Game mechanics: the rules and systems that govern how players interact with the game.
- Game dynamics: the emergent patterns of behavior that arise from the interaction between the mechanics and the players.
- Game aesthetics: the visual and auditory elements that contribute to the player’s experience.
B. Importance of game design
Game design is essential to the success of any game. A well-designed game can engage players for hours, creating a sense of challenge, immersion, and enjoyment. Good game design can also help to create a unique identity for a game, setting it apart from other games in the same genre.
Moreover, game design can influence players’ behavior and attitudes. For example, a game designed to teach history can help students learn about the past in an interactive and engaging way. Similarly, a game designed to promote empathy can help players understand and appreciate different perspectives.
C. Brief history of game design
Game design has been around for thousands of years, with early examples including board games, card games, and dice games. However, the modern era of game design began in the mid-20th century with the development of electronic games.
The first electronic game, Spacewar!, was developed in 1962 by a group of MIT students. Since then, game design has evolved rapidly, with new technologies and platforms enabling more sophisticated and complex games.
Today, game design is a multi-billion dollar industry, with millions of people playing games on a variety of platforms, including consoles, computers, and mobile devices. Game design continues to evolve, with new trends emerging and new technologies pushing the boundaries of what is possible.

II. Elements of Game Design
Game design is both an art and science that involves the careful combination and balance of various elements to create interactive experiences that are enjoyable, engaging, and often, challenging for players. The craft revolves around several core components – Mechanics, Dynamics, and Aesthetics – which collectively form the backbone of any successful game. Let’s take a closer look at each one:
A. Mechanics
Mechanics refers to the rules and systems that guide the gameplay. It includes everything from the basic controls that allow players to interact with the game world to complex systems that dictate how in-game entities behave or interact with one another. In essence, mechanics define what actions players can take within the game, how they can perform them, and what outcomes those actions can lead to.
Next are some Examples of game mechanics usually used in games:
- Movement: How the player character moves through the game world. For example, running, jumping, and climbing.
- Combat: How the player engages in combat with enemies. For example, turn-based combat or real-time combat.
- Puzzles: How the player solves puzzles or challenges within the game. For example, unlocking a door or completing a maze.
- Resource Management: How the player manages resources such as health, ammunition, or money. For example, choosing when to use a health pack or saving money to purchase a better weapon.
B. Dynamics
Dynamics are created by running mechanics over time. They represent the behavior of the entire system when players influence it through their actions. This could be something as simple as chasing an opponent around a map or as complex as managing resources in a strategy game. Dynamics also encompass interactions between multiple mechanics, generating emergent gameplay scenarios that add depth and richness to the player experience.
Below are some Examples of game dynamics that can be used in games:
- Player Choices: How the player’s choices and actions affect the game world and its story. For example, choosing to spare or kill a character may impact the game’s ending.
- Emergent Gameplay: How the player’s actions and decisions lead to unexpected and unique situations within the game. For example, in a sandbox game, players may create their own challenges or goals.
- Difficulty Curve: How the game’s difficulty ramps up over time, providing players with an appropriate challenge as they progress through the game.
C. Aesthetics
Lastly, Aesthetics refers not only to visual representation but also to sound design, musical score, storyline & narrative structure – all aiming at eliciting emotional responses from players. It is important because it provides context for player actions by creating a sensory environment in which gameplay takes place.
Examples of game aesthetics include:
- Art Style: How the game looks and feels visually. For example, a game may have a cartoonish art style or a more realistic one.
- Music: How the game’s music enhances the emotional impact of the game. For example, a game may use music to create tension or to evoke a sense of adventure.
- Sound Effects: How the game’s sound effects contribute to the player’s experience. For example, the sound of a gun firing or the sound of footsteps can add realism and immersion to the game.
- Storytelling: How the game’s narrative is conveyed to the player. For example, a game may have a linear story with cutscenes or a more open-ended story that is discovered through exploration.
Together these elements combine seamlessly to produce games that capture our imagination and keep us hooked for hours on end. Mechanics, Dynamics, and Aesthetics are the three core elements of game design that work together to create an engaging and immersive experience for players. A game designer must carefully balance these elements to create a cohesive and enjoyable game.

III. Game Design Process
Game design is a complex and iterative process that involves many stages, from generating ideas to Playtesting and iteration. Without a solid design process, a game can easily become a confusing mess that fails to engage or entertain players. A well-designed game, on the other hand, can be a masterpiece that captivates players and keeps them coming back for more.
We’ll examine the game design process, including its key stages, and provide tips for creating a successful game.Whether you’re a seasoned game designer or a newcomer to the field, understanding the game design process is essential for creating compelling and successful games.
A. Idea generation
- Brainstorming: Brainstorming is a technique used to generate many ideas in a short amount of time. In game design, it is used to come up with game concepts, gameplay mechanics, and other creative ideas. During brainstorming, there are no bad ideas, and the goal is to generate as many ideas as possible without self-censorship. This technique can be done individually or in a group and can involve different methods such as mind-mapping or free-writing.
- Research is a crucial step in game design. It includes studying the audience, analyzing similar games, and staying updated on the latest design trends.This research helps game designers to create games that appeal to their audience, and it can help them avoid making mistakes that other game designers have made in the past. Some of the areas of research can include market analysis, player behavior, game mechanics, and narrative structures.
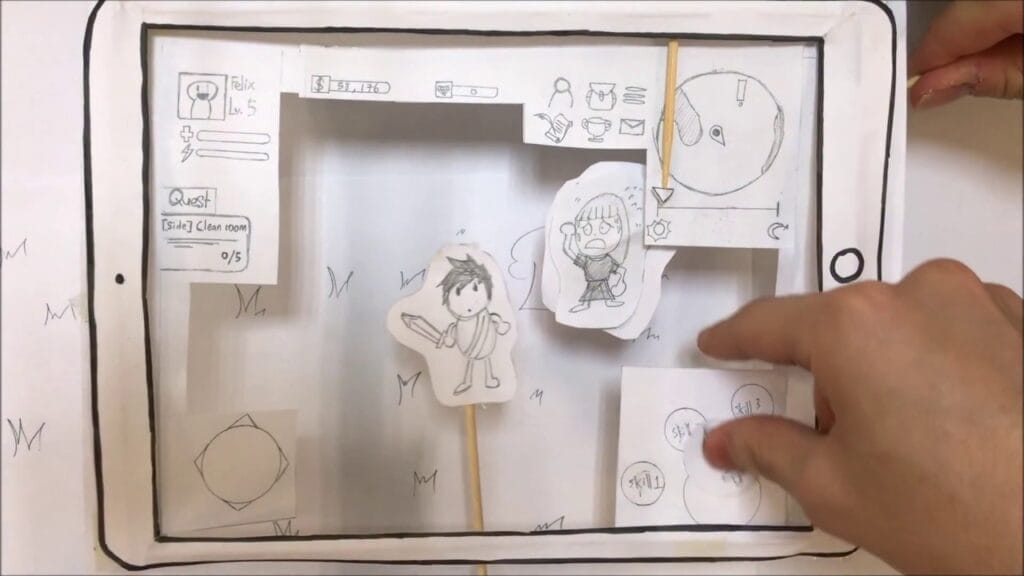
B. Prototyping
- Paper prototyping: Paper prototyping is a technique used to quickly create and test game mechanics before creating a digital prototype. This technique involves drawing the game’s interface and mechanics on paper and using paper cutouts to represent game objects. This technique allows game designers to test their game mechanics and make changes before investing time and resources into a digital prototype.
- Digital prototyping: Digital prototyping is the process of creating a functional version of the game, usually with the use of game engines and software tools. The prototype can vary from a basic version with only game mechanics to a polished version with graphics, audio, and improved gameplay that includes only the game’s basic mechanics to a more polished version that includes graphics, audio, and more refined gameplay.
C. Playtesting
Playtesting is the process of testing a game with real players to identify and fix issues and improve the gameplay experience. Playtesting can involve observing how players interact with the game and gathering feedback from players. It can be conducted in different stages of the game design process and can involve different types of players, such as experts or novices.
Playtesting is a critical step in game design, as it helps game designers identify issues and make changes before releasing the game. Playtesting can help game designers identify areas where players get stuck or frustrated, where the game mechanics may not be clear, or where the game’s difficulty may be too high or too low. This feedback can help game designers improve the gameplay experience and create a more engaging game.
D. Iteration
Iteration is the process of making changes to the game based on feedback from playtesting or other sources. Iteration can involve making changes to game mechanics, graphics, audio, and other aspects of the game.
Iteration is an essential part of the game design process, as it allows game designers to refine their game and make improvements based on feedback from playtesting or other sources. Iteration helps ensure that the game is engaging and enjoyable for players and that it meets the expectations of its target audience. Without iteration, a game may fail to meet the needs of its players, leading to poor reviews and low sales.

What is game design – Unity as an important game design tool Source:unity3d
IV. Game Design Tools
Game design tools are essential for creating games. These tools range from game engines to art and sound design software. In this section, we’ll explore some of the most popular game design tools and their functions.
A. Game Engines
Game engines are software frameworks that provide developers with the necessary tools to create video games. They often include a variety of features such as physics engines, scripting tools, and visual editors to create levels, characters, and environments. Here are some examples of popular game engines:
- Unity: Unity is a popular game engine used to create 2D and 3D games across multiple platforms, including desktop and mobile devices. Unity supports a variety of programming languages, including C#, JavaScript, and Boo.
- Unreal Engine: Unreal Engine is a game engine developed by Epic Games that is used to create high-quality 3D games. It features a powerful visual editor, a robust physics engine, and supports multiple platforms, including consoles and mobile devices.
- Godot: Godot is a free and open-source game engine that is easy to use and can be used to create both 2D and 3D games. It features a user-friendly interface, a powerful scripting language, and supports multiple platforms.
B. 2D and 3D Art Tools
Game designers use 2D and 3D art tools to create characters, objects, and environments for their games. These tools can range from basic drawing software to more advanced 3D modeling software. Here are some examples of popular 2D and 3D art tools:
- Adobe Photoshop: Adobe Photoshop is a popular raster graphics editor that can be used to create 2D art for games. It features a variety of tools for drawing, painting, and editing images.
- Blender: Blender is a free and open-source 3D creation software that is often used by game designers to create 3D models for their games. It features a powerful modeling toolset, animation tools, and a built-in game engine.
- Autodesk Maya: Autodesk Maya is a 3D animation and modeling software used by game designers to create high-quality 3D models, animations, and visual effects. It features a robust toolset for modeling, texturing, and animating 3D assets.
C. Sound Design Tools
Sound design is an essential component of game design, and sound design tools are used to create sound effects, music, and dialogue for games. Here are some examples of popular sound design tools:
- Fmod: Fmod is an audio middleware software used by game designers to create interactive sound effects and music. It features a powerful audio engine, a user-friendly interface, and supports multiple platforms.
- Wwise: Wwise is another audio middleware software used by game designers to create interactive sound effects and music. It features a variety of tools for mixing, mastering, and integrating sound into games.
- Audacity: Audacity is a free and open-source audio editor used by game designers to edit and manipulate sound effects and dialogue. It features a variety of tools for recording, editing, and processing audio.
V. Game Design Careers
A. Game Designer
Game designers are responsible for creating the vision and overall concept for a game. They work with a team of artists, programmers, and other game developers to ensure that the game is both engaging and enjoyable for players. Some of the key responsibilities of a game designer include:
i. Responsibilities
- Creating the game concept and design documents that outline the mechanics, story, characters, and overall gameplay
- Collaborating with artists, programmers, and other developers to ensure that the game design is properly implemented
- Testing the game and making adjustments as needed to ensure that it is enjoyable and challenging for players
- Conducting research on industry trends, player preferences, and other relevant factors to inform the game design process
- Communicating with stakeholders and team members to ensure that everyone is aligned on the game design vision and goals
ii. Skills required
- Creativity and imagination to come up with unique game concepts and mechanics
- Strong communication skills to collaborate effectively with other team members and stakeholders
- Analytical thinking and problem-solving skills to identify and address issues with the game design
- Knowledge of game mechanics, game theory, and user experience design principles
- Familiarity with game development tools and software, such as Unity, Unreal Engine, or GameMaker Studio
B. Game Artist
Game artists are responsible for creating the visual elements of a game, including characters, environments, and other assets. They work closely with game designers to ensure that the visual style of the game aligns with the overall design concept. Some of the key responsibilities of a game artist include:
i. Responsibilities:
- Creating 2D or 3D models of characters, environments, and other game assets
- Texturing and shading game assets to create a cohesive visual style
- Animating characters and other game elements to bring them to life
- Collaborating with game designers and other developers to ensure that the visual style of the game aligns with the overall design concept
- Creating concept art and storyboards to communicate design ideas to the rest of the team
ii. Skills required
- Strong artistic skills, including drawing, painting, and 3D modeling
- Familiarity with industry-standard design software, such as Photoshop, Maya, or Blender
- Knowledge of animation principles and techniques
- Attention to detail and a keen eye for aesthetics
- Creativity and the ability to come up with unique visual concepts and designs
C. Game Programmer:
Game programmers are responsible for implementing the game design in code. They work closely with game designers and artists to ensure that the game mechanics are properly implemented and that the game runs smoothly. Some of the key responsibilities of a game programmer include:
i. Responsibilities:
- Writing code to implement game mechanics, controls, and other features
- Optimizing game code to ensure that the game runs smoothly on various platforms and devices
- Collaborating with game designers and artists to ensure that the game design is properly implemented in code
- Debugging and testing game code to identify and fix issues
- Staying up-to-date with industry trends and best practices for game programming
ii. Skills required:
- Proficiency in programming languages commonly used in game development, such as C++, C#, or Java
- Familiarity with game development tools and software, such as Unity or Unreal Engine
- Strong problem-solving skills and the ability to debug code effectively
- Attention to detail and the ability to write efficient and optimized code
- Good communication skills to collaborate effectively with other team members
Conclusions: What is game design
In this article, we have taken a look at what is game design from several different point of views:
- Game design is the process of creating the rules, mechanics, aesthetics, and dynamics of a game.
- Game design involves a process that includes idea generation, prototyping, playtesting, and iteration.
- Game designers use tools such as game engines, art tools, and sound design tools to create games.
- Game design is an interdisciplinary field that involves game designers, game artists, and game programmers.
- Game design is important because it affects the player’s experience and determines the success of the game.
B. Future of game design: In this section, you can discuss the future of game design and how it might evolve. Some potential ideas to discuss include:
- The increasing use of virtual and augmented reality technologies in game design.
- The growing importance of mobile gaming and the need for games that can be played in short bursts.
- The rise of esports and the importance of designing games that can be played competitively.
- The potential for game design to be used in fields beyond entertainment, such as education, healthcare, and training.
Reading is not enough to become and get a job as a game or level designer in the games industry, you need to take action based on the information in the post:
- Try your own take at game design by experimenting with game engines or creating a simple paper prototype.
- Explore job opportunities in game design or consider pursuing education or training in the field.
- Support independent game developers and seek out and play games made by smaller studios or solo developers.
- Stay up-to-date on developments in the field of game design by following industry news or attending conferences and events.
What are your thoughts on this matter? Have we missed some specific point that you would like to see? Why don´t you share your own opinion in the comments sections?
Also, don´t forget to come back regularly to our blog, as we are constantly updating it with new content.





















